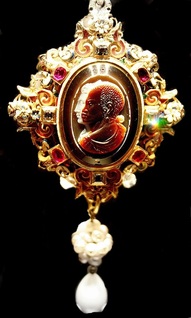
 The Drake Jewel (V&A)
The Drake Jewel (V&A) A few days before my talk, the poet Benjamin Zephaniah had been quoted by the BBC as saying that black and Asian pupils are turned off history because they are told only "half the story" in British schools.
The same BBC article reported that Education Secretary Michael Gove "has said schools should focus on a traditional narrative of British history in response to concerns it had become too politically correct [and]... that the current approach to history denies 'children the opportunity to hear our island story', and... this has to change."
Continue reading the main story... the current approach to history denies "children the opportunity to hear our island story", and this has to change."The phrase "our island story" jumped out at me because it reminded me of an old book I'd grown up with. Our Island Story is a nostalgic, patriotic storybook written in Australia in 1905 by Henrietta E. Marshall. This Edwardian tome was reprinted in 2005 by the think-tank Civitas, with the aim to send a free copy to each of the UK's primary schools. David Cameron told the RSC it was his favourite childhood book in 2010, and that it "really captured [his] imagination and ... nurtured [his] interest in the history of our great nation.” But what stories does this book tell? And are they really only "half the story"?
Take Sir Francis Drake, for example. A classic Elizabethan hero, he appears of course in Our Island Story, where Marshall describes him as "very bold and daring", and tells the story of the singeing of the King of Spain's beard, and him refusing to face the Armada before he'd finished his game of bowls on Plymouth Hoe. But my research has shown me another side of Drake, that is writ large upon the Drake Jewel (above, a present from the Queen in 1588, which Drake wore hanging from his belt in this 1591 portrait) but that is not included in Marshall's version of events.
The bust of an African man on the Drake jewel has been interpreted as a symbol of Drake's alliance with the Cimaroons. These were the Africans who had runaway from the Spanish who had enslaved them and set up their own communities. Their local knowledge was invaluable to Drake when he allied with them to capture the Spanish silver train in Panama in 1573. One of these Cimaroons, a man named Diego, returned to Plymouth with Drake and accompanied him on his circumnavigation voyage of 1577-80. Unfortunately he died near the Moluccas, from wounds received from the hostile inhabitants of Mocha Isle, off the coast of Chile.
Diego was not the only African onboard. We know of at least three more, one of which, a woman named either Francesca or Maria, who was abandoned, heavily pregnant, on Crab Island, Indonesia. William Camden, the first historian of Elizabeth I's reign, reported in his Annales that Drake "purchased much blame…for having most inhumanely exposed in an island that negro or blackamore maid who had been gotten with child in his ship.” However this, and other stories of Africans who encountered Drake, seem to have disappeared from popular record.
Drake's cousin, John Hawkins doesn't appear in Our Island Story at all. Drake may well have accompanied him on some of his slaving voyages in the 1560s. And later voyages that Drake made to the Caribbean, for example his raid of 1585-6, also resulted in Africans coming to England.
The idea of "Our Island Story" needs to be re-imagined. To be 'insular' can mean to be cut off from the rest of the world. But the histories of most islands, from Crab and Mocha isles, mentioned here, to the Island of Britain, are stories of comings and goings, of invaders and immigrants. The story of our island is one of these. And we need to tell our children the whole story, and to do so we need to re-tell it for our time and not rely on the imaginings of an Edwardian patriot, however picturesque.


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
